Hip dysplasia is one of the most common mobility difficulties in dogs, especially large ones. At Ortocanis, we work every day to expand and improve our range of products for these types of problems, and we believe that any additional information is good. Here we leave you another interesting article.
At the University of León, a radiographic method has been developed for the early diagnosis of this disease with great emotional repercussions for owners.
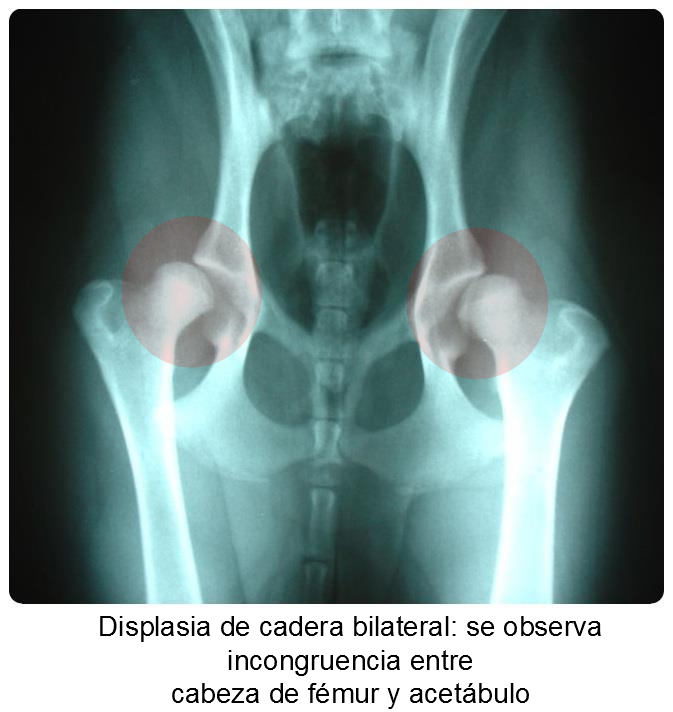
Hip dysplasia is a very common disease in large and giant breeds of dogs, which consists of defective development of this joint.
In it, the two bones that form the joint, femur and pelvis, do not adapt correctly due to different biomechanical imbalances produced during the growth of the animal. It is a hereditary disease, so the main solution to eradicate it is to avoid breeding these animals, although it is also important to control factors such as nutrition, weight or overexertion of the puppy during its growth as well as consanguinity in selective breeding.
The symptoms presented by the animals vary according to the severity of the dysplasia, from a slight lameness to the total inability of the animal to lead a normal life.
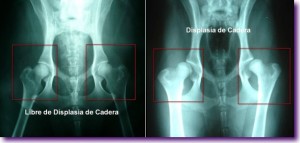
The diagnosis of this disease is not easy, since there is no method that allows it to be determined in all cases. The method accepted in Spain for certificate purposes is radiographic, although it has the disadvantage that it must be carried out when growth has finished, that is, after twelve months for most breeds.
Early diagnosis can prevent transmission
In the Doctoral Thesis of Beatriz Melo Alonso, defended at the University of León and directed by doctors José Manuel Gonzalo Orden and Mario Manuel Dinis, hip dysplasia has been investigated in one of our native breeds: the Burgos Pointer.
The result of this research has been worrying, since 59.3% of the animals studied suffer from hip dysplasia in its different degrees, with 18.6% severe dysplasia. This high percentage should alert the Burgos Perdiguero associations to try to eradicate it.
Early diagnostic
The drawback is that the aforementioned diagnostic technique is very late, and therefore, has a great emotional impact on owners.
For this reason, another part of the research has consisted of perfecting, for this breed, a new diagnostic technique developed in the United States called the PennHIP or distraction method, which consists of taking a specific X-ray and taking a measurement on it called the index of distraction.
This study has concluded that with the PennHIP method this disease can be predicted from four months of age, and throughout the animal’s growth, with the same reliability, in the Pointer, and it has even been possible to enunciate a formula with the which will know the degree of hip dysplasia that he will have in the future from the distraction index that he presents at four months. This system could reduce this disease, which has so much repercussion, both on the animal itself and on the owners.
Source: University of León








 can help us a lot to improve muscle mass that can make us better withstand poor joint congruence, physiotherapy and massages allow the dog to always have a correct muscular state, cartilage protectors delay the onset of osteoarthritis, anti-inflammatories prevent or reduce pain, we can protect the dog from the cold with
can help us a lot to improve muscle mass that can make us better withstand poor joint congruence, physiotherapy and massages allow the dog to always have a correct muscular state, cartilage protectors delay the onset of osteoarthritis, anti-inflammatories prevent or reduce pain, we can protect the dog from the cold with 
