Elbow dysplasia in dogs
Elbow dysplasia is a very common degenerative disease in young dogs.
The elbow of dogs is one of the most congruent and stable joints of the body, allowing, due to its complexity, two axes of or degrees of supination-pronation movement of the forearm and flexion-extension. Its complexity is given by its composition: humeroradial joint, humeroulnar and, proximal radioulnar.
Elbow dysplasia was initially used to describe the non-union of the anconeal process (AUP). Currently, osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) of the medial condyle of the humerus, the fragment of the coronoid process (FPC) and, the incongruence of the elbow (INC) are also included within this term. When one of these ossification defects occurs in an elbow, inflammation originates and over time an osteoarthritis is triggered in which cartilage degeneration occurs; for that reason, all these conditions are commonly associated with osteoathrosis of this joint and are an important cause of pain and claudication of the forelimbs in large and giant breed dogs such as the German Shepherd, Labrador, St. Bernard, Rottweiler, Neapolitan Mastiff, among others.
Of multifactorial genetic origin, especially in OCD and FPC. It affects males more than females and can occur uni- or bilaterally. The genetic component is the one that has the greatest influence although, the appearance of this pathology can also occur due to food, weight, environment, quality of ligaments, a lot of physical exercise or trauma.
The first symptoms may occur at 4-5 months when the dog shows exercise intolerance, lameness when starting a movement or after prolonged exercise. There are dogs that do not show signs of affection in the elbow until advanced ages where the process of osteoarthritis is very evolved. Others manage to maintain a normal degree of activity throughout their lives.
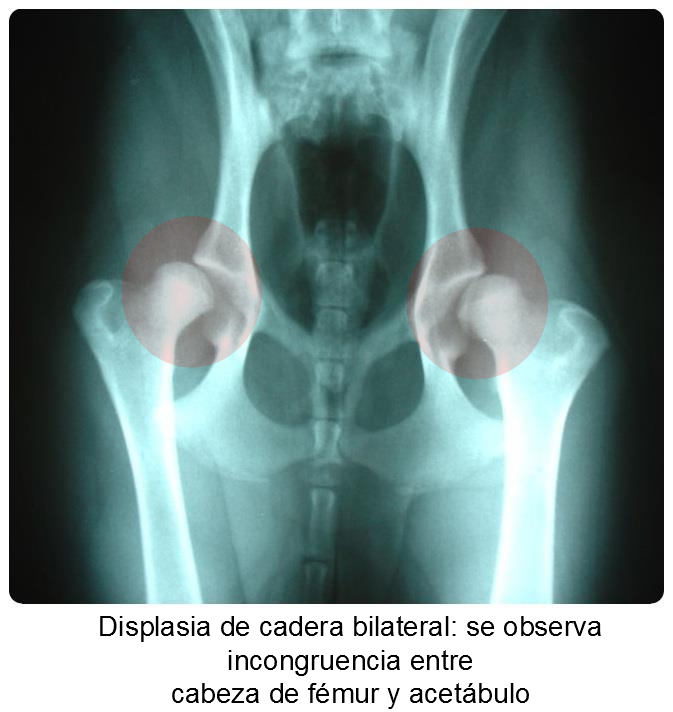
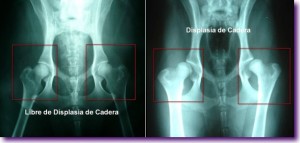
The fact of making a premature radiological diagnosis makes it possible to establish an adequate treatment and avoids the formation of osteoarthritis that produces pain and functional limitation of the elbow throughout the life of the animal. The diagnosis can be complemented with diagnostic tests such as CT or MRI
The evolution depends on the degree and type of injury, but it is usually unfavorable without surgery. Surgical treatment is good if degenerative changes in the joint have not yet occurred. In any case it is necessary to perform a good rehabilitation in order to:
- Speed up the recovery process
- Eliminate pain and inflammation
- Decrease lameness
- Maintain and/or improve range of motion
- Maintain muscle tone, mass and strength
- Minimize or slow down the effects of joint degeneration – osteoarthritis
- Avoid compensation at the level of the neck, spine and extremities
- Give the maximum capacities so that the animal is functional and that it, with a good quality of life
Physiotherapy treatment varies depending on the animal and the state of the lesion. It is important to start as soon as possible with the treatment so that it is effective and, to avoid drying them as reduced mobility and / or chronic pain.
The animal goes through different phases until its full recovery. It is essential to gradually achieve the objectives set. The recovery process is terminated when the animal is able to perform daily activities.
During the first three days after the intervention, it is important to act on inflammation and pain and prevent muscle atrophy and decrease in the joint arch from appearing. For this, passive techniques are used that reduce inflammation, produce analgesia and help maintain tone, mass and the arc of mobility. Among these techniques there are electrotherapy (segmental TENS and muscle electrostimulation), massage, passive mobilizations and cryotherapy (cold).
In older dogs or dogs that have not been intervened, the objectives will be the same as in animals that have gone through an intervention. It is important to eliminate pain because, with pain you can not work.
It is important from the beginning to massage and move the affected elbow as long as there is no veterinary contraindication and, respecting in the case of fixation, the period of healing and union of the fixed parts. Massaging and moving the affected area and limb helps maintain mobility, prevents loss of mass and tone and works the proprioceptors.
 A gentle mobilization combined with different massage techniques help decrease inflammation and reduce pain.
A gentle mobilization combined with different massage techniques help decrease inflammation and reduce pain.
With TENSat the segmental level we can produce analgesia and decrease the amount of drugs administered. There are animals that have intolerance to certain drugs that produce analgesia and with TENS the pain can be reduced. TenS can also be used directly on the injured or operated area, as long as there is no osteosynthesis material underneath, since an internal burn could occur.
Muscle electrostimulationhelps prevent the onset of atrophy and maintain muscle mass and tone. With electrical stimuli we can stimulate nerve conduction.
At the beginning and end of the session the coldis used since it has properties that act on the decrease of the inflammatory response, edema and pain.
From the fourth day and during the next two weeks when the inflammation and pain have disappeared it is time to introduce simple active exercises such as shaking hands or small walks on a leash to force the animal to make an equal support with the four limbs and thus, prevent a decompensation between limbs from appearing due to not having a correct support on the ground. The walks is an exercise that increases the duration until full recovery.
Once the stitches have been removed, the animal can be introduced into the water. The advantages of water are used to improve recovery. Hydrotherapy (underwater treadmill) facilitates the station of the animal without loss of balance and, thanks to flotation, without having to support all its weight. In addition, flotation allows animals with bone pain and low muscle mass to work. The pressure of the water exerted on the body of the animal increases the sensitivity and decreases inflammations and edemas. The work in the water, underwater tapes or swimming increasesas the animal recovers. In addition, with water, we can recover the motor pattern, increase mass, tone and strength, work on respiratory capacity and maintain and / or improve mobility.
Once the acute phase has passed 48-72 hours and without risk of infection or inflammation, heat can be introduced that helps to elastify the tissues, decreases pain and increases vascularization among others.
The use of boards, plates, balls and trampolines are important to work on balance, proprioception and above all the integration of the affected limb.
It is already in the last phase, from two weeks, when the dog has integrated the gait pattern, exercises are performed to improve the quality of movement. They are more complex active exercises to integrate the affected limb or limbs. With active and proprioception exercises it is possible to increase muscle tone, mass and strength; coordination and balance and range of motion are worked on. Rails with different surfaces, cones, bars, circuits, up and down stairs and ramps (staircase with inclined plane) are used.
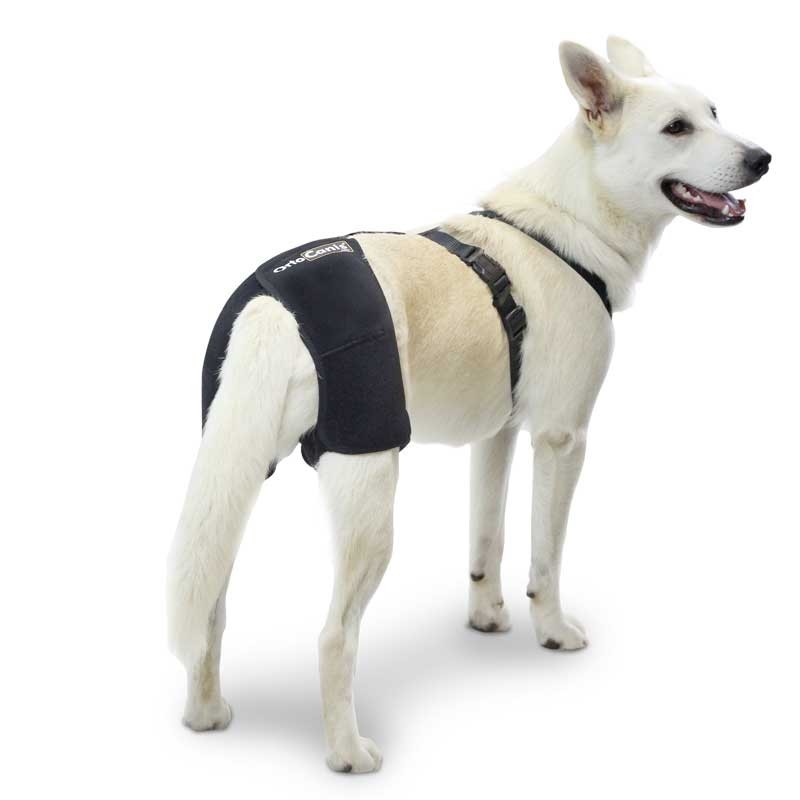
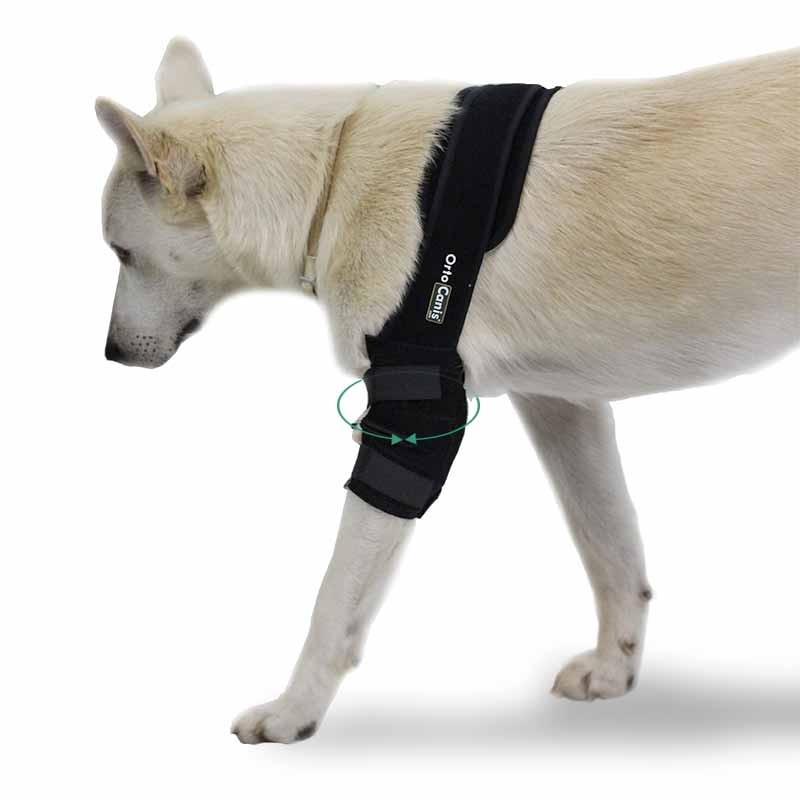
Throughout the recovery treatment and in animals with developed osteoarthritis it is essential to reduce the weight on the joints of the elbows. For this purpose , special support harnesses for elbows are used. In addition to decreasing weight, pain is reduced and does not hinder movement, the animal feels more comfortable; the joint is protected at all times from chafing and blows and helps maintain the heat that the animal gives off, which leads to a relief of the affected area.
At home, special care should be taken for animals suffering from elbow conditions. This care is necessary during and after treatment:
- Avoid slippery floors
- Avoid ramps and stairs at the beginning of treatment in operated animals and in animals that do conservative treatment. Once rehabilitated, ramps can be used to help get on the sofa and the car, since it is recommended that they do not do it alone, there could be a recidivism.
- It is recommended that they rest on soft and clean surfaces, but that they are firm enough to help the incorporation of the animal special mattress for dogs
- Keep skin clean and dry skin
- Use special plates at your height so as not to strain the elbow joints
- Correct diet and weight control. Being overweight harms the joints and generates more pain for the animal
It is very important to create an exercise routine and environment to help keep the animal comfortable and with quality of life.
You can also check:
Can chondroprotectors help?
Elbow dysplasia in dogs
Hip dysplasia in dogs