Hip dysplasia is a very common problem in certain breeds: BullDog, Bordeaux Doge, St. Bernard, Neapolitan Mastiff, German Shepherd, Rottweiler, Golden… all of them have an incidence above 20%.
Dysplasia is a multifactorial, multigenic and hereditary disease, that is, there are several factors that predispose and cause hip dysplasia, there are several genes involved in its appearance and it has a hereditary character.
Environmental factors are becoming more and more important in the development of hip dysplasia, the genetic factor is necessary to develop the disease but this is not the only factor. Genetics is a necessary but not exclusive factor, that is, you can have the genetic predisposition and not develop the disease but if you do not have a predisposition it is sure that it does not develop.
There are several degrees of dysplasia, and also those that appear when the dog is a puppy or those that give problem already in adulthood; but in this article we will focus on the treatment and specifically on the treatment of dysplasia to young dogs.
Classification of the degrees of dysplasia according to the OFA :
Grade I: minimal alteration with small subluxation and few degenerative changes.
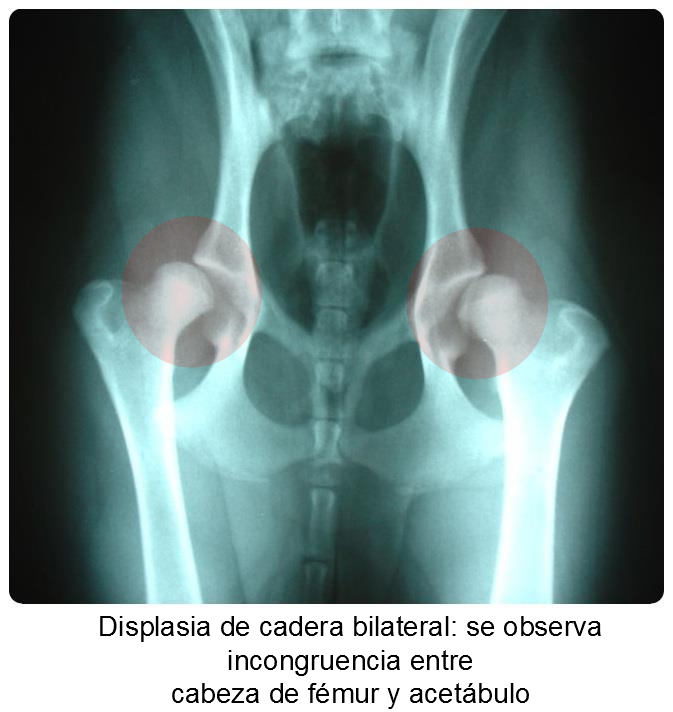
Grade II: marked lateral subluxation of the femoral head, 25-50% of which is outside the acetabulum.
Grade III: 50-75% of the femoral head is outside the acetabulum; there are important degenerative changes.
Grade IV: dislocation of the femoral head with flattening of the acetabular border and femoral head; there are major degenerative changes.
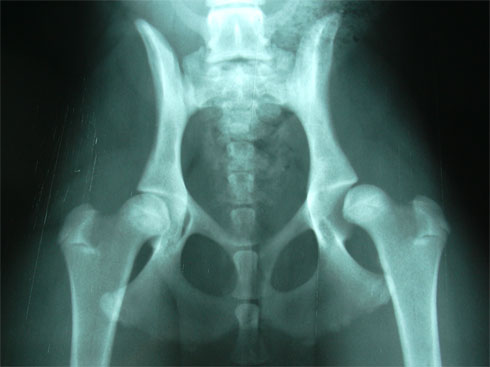
The presentation in the young dog is puppy hip x-ray normally between 5 and 6 months and is marked by a significant limp.
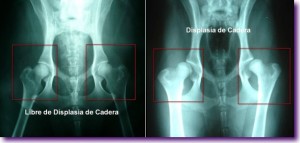
A dog is not considered to be free of dysplasia until at two years of age already completed no problems or inconsistencies are observed in the control x-rays.
Food is one of the factors that predisposes to the appearance of hip dysplasia, Calcium-Phosphorus imbalances that must keep a correlation Ca1.6% – P1.1% and above all not overfeeding or providing excess proteins allows us to minimize the incidence of hip dysplasia. A hypocaloric diet from 3 months to 8 months protects dogs with rapid growth from dysplasia. Excess weight at 60 days is another factor that predisposes to the disease.
Hip dysplasia in the puppy usually debuts from 5 or 6 months, before it is not possible to observe any problem and the dog has been completely normal and has developed normally. The debut is usually presented as a sharp limp that prevents the dog from playing as it had done to date. We can observe changes in the desire to play, negative when going for a walk, to relate to other dogs or owners. Mood swings, frequent slips of the hind legs, discomfort and even refusal to be touched and the fact of “fleeing” from children in dogs that until a few days ago were playful and affectionate are frequent.
Sometimes when you reach 90% of the growth between 8 and 11 months the signs can be reduced and even disappear. Anyway the dysplasia remains and in many cases the problems reappear after a while and sooner rather than later signs of osteoarthritis appear in the hips.
The most common clinical signs are:
Lameness that may increase with exercise
Walking and jogging with hip swing
Morning stiffness
Difficulty getting up
Muscle atrophy
Refusal to move
Mood swings
Pain on palpation
Sign of Ortolani.
Although there are surgical methods: excision of the pectineus muscle, triple hip osteotomy, arthroplasty of the femoral head, osteotomy of the pubis, forage, hip prostheses most are practiced when the dog is young to supposedly decrease the possibility of secondary coxofemoral osteoarthritis in adulthood. The hip prosthesis should be reserved for severe cases and once the growth has finished.
Medical treatment is based on anti-inflammatories, we can start with natural anti-inflammatories, such as inflamex, which does not contain medicinal substances, if we do not obtain the expected results move to Aine’s and in extreme cases corticos are resorted to. We must include nutraceuticals especially chondroprotectors since they reduce the incidence of osteoarthritis and protect the articular cartilage. These are used in senior dogs in a very general way but are very useful as a joint protector in growing dogs, there are specific drug carriers for young dogs. Weight reduction, moderate and above all regular exercise are other basic points, as well as improvements in the environment and the fact of sleeping on a special mattress for older dogs and in a warm place away from humidity.
Canine physiotherapy can help a lot to better develop the muscles to reduce pain, to draw tensions and eliminate compensations that the dog has made with the wrong postures and antialgic positions. This will be based on TENS, ultrasound, therapeutic exercises, the use of hydrotherapy, laser, shock waves…
The main improvement in the environment is to sleep on a good therapeutic mattress, not to be cold or exposed to a lot of humidity, to use in winter a thermal coat for dogs, to be able to be a therapeutic canine blanket that can be used all year round.
We can help our Dog with hip dysplasia, regular physical exercise can be very useful to improve muscle mass that better withstands poor joint congruence, avoid impacts, jumps or uncontrolled runs during the presentation of the picture are also important elements. Physiotherapy and massages allow you to always have the dog in a correct muscular state, and all the adjuvant treatments such as acupuncture, massages, reiki, bach flowers … they can also help with treatment. The latest novelty is the hip supports that help stabilize the pelvis, give support and greatly improve the quality of life of our pets.
Toni
Ortocanis.com Team
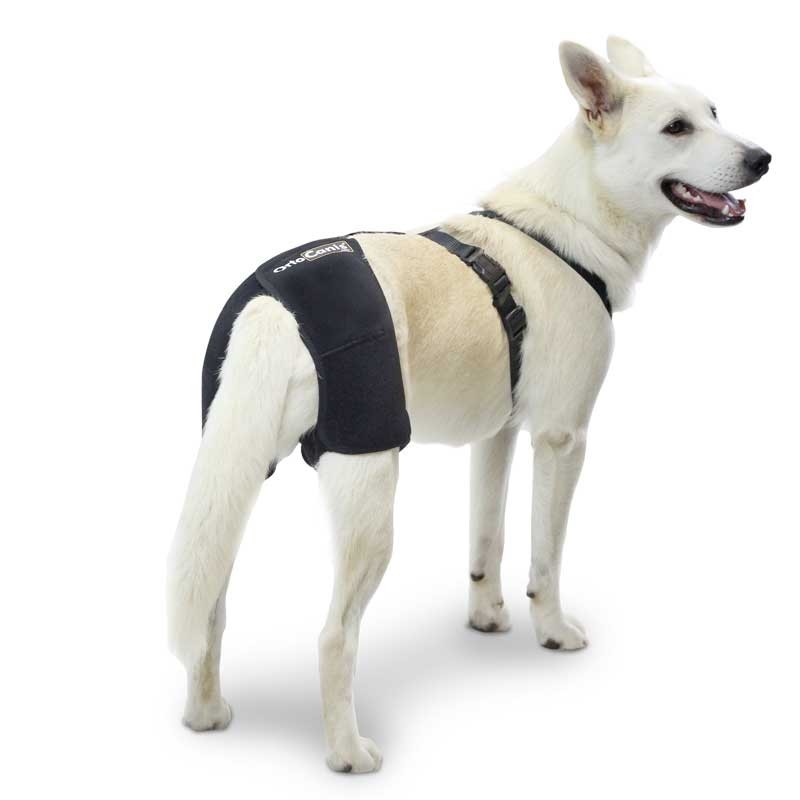












 can help us a lot to improve muscle mass that can make us better withstand poor joint congruence, physiotherapy and massages allow the dog to always have a correct muscular state, cartilage protectors delay the onset of osteoarthritis, anti-inflammatories prevent or reduce pain, we can protect the dog from the cold with
can help us a lot to improve muscle mass that can make us better withstand poor joint congruence, physiotherapy and massages allow the dog to always have a correct muscular state, cartilage protectors delay the onset of osteoarthritis, anti-inflammatories prevent or reduce pain, we can protect the dog from the cold with