Canine osteoarthritis is a very common disease in dogs. It appears as a result of the inevitable evolution of a joint that ages or becomes increasingly fragile due to trauma or malformation. This is a very painful condition that needs to be treated right away. It can affect all the joints of the body, both those found in the anterior and posterior extremities, as well as those that form the spine. In the case of senior dogs, the most common is that this disorder affects several joints at once.
The articular surface is covered by a tissue called cartilage, which plays a role very similar to the shock absorbers found in cars. In addition, it prevents the underlying bone from deteriorating due to the repeated rubbing to which it is subjected by continuous movement. Osteoarthritis is characterized by a progressive destruction of this cartilage and by an abnormal bone proliferation at the edge of the articular surfaces known as osteophyte, also called ‘parrot beaks’ when they are located in the spine. The affected joints lose elasticity, cause pain and prevent the animal from moving normally.
Evolution of deterioration
As a rule, this ailment affects, first of all, the high joints of the limbs: hips and knees, shoulders and elbows. Symptoms are more or less important depending on the number of joints affected. However, there is an unequivocal sign that makes us intuit that the animal is affected. Lameness usually manifests itself when the dog gets up and starts up after remaining immobile for a long time.
The pain prompts the animal to avoid support on the affected limb and, being impeded, stops running, and of course, jumping. As it evolves, the pain increases. When making certain movements, the dog emits small moans, it is even possible that the animal is irascible and tends to present aggressiveness when we try to manipulate the affected joint.
In more advanced cases, the joint may be partially blocked, making it impossible to perform certain movements. At this point, the animal hesitates to use the diseased limb. In addition, this lack of activity leads to a significant deterioration of the musculature surrounding the joint. As a result, the diseased area begins to atrophy, which increasingly complicates its use.
Two fundamental types
As a general rule we distinguish two types of osteoarthritis: primary and secondary. The first type usually affects elderly animals and appears due to the normal aging suffered by the joints due to the passage of time. In fact, it is a progressive and inevitable wear of the articular cartilages. Usually, this type of osteoarthritis affects different points at the same time.
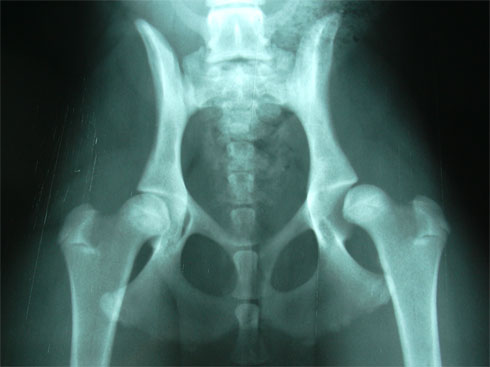
As far as secondary canine osteoarthritis is concerned, it appears as a consequence of a triggering factor, which causes the affected joint to stop functioning normally. For example, this type of osteoarthritis can appear due to trauma – a sprain, a fracture, etc. – or due to a birth malformation, such as hip dysplasia.
Another very common cause that causes the appearance of secondary osteoarthritis is obesity. If you do not control the diet your friend can have a weight well above the average that we find in the breed. The joints are not made to support such a significant overload of kilos, so they deteriorate easily. Unlike primary osteoarthritis, secondary osteoarthritis can affect animals of all ages and, as a general rule, usually affects only one joint.
Issue a diagnosis
The diagnosis of this disease can be based on three factors: the pathological history of the animal, gait examination and manipulation. When studying the history, the veterinarian must take into account old joint fractures, injuries that the animal has suffered a long time ago, as well as possible sprains. When observing the gait will look at whether the dog limps, even if only very slightly and incipiently, since lameness is an unequivocal symptom of the disease. Finally, when manipulating the affected area it is very possible for the animal to show signs of pain.
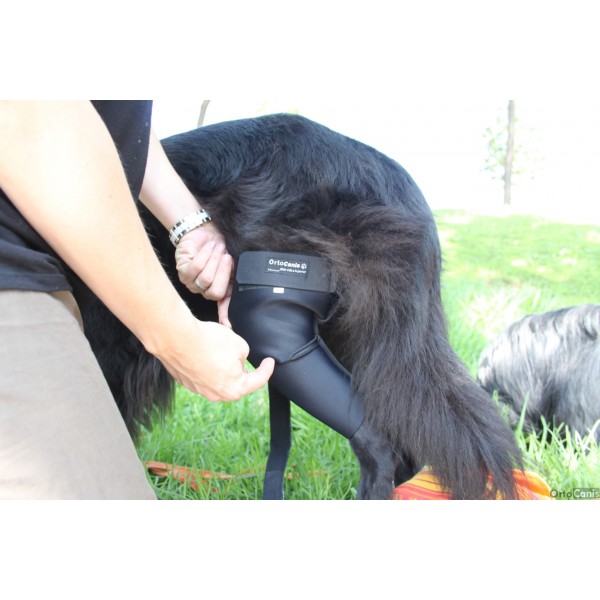
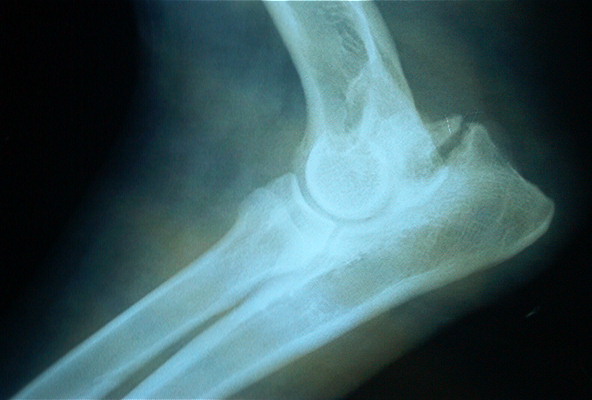
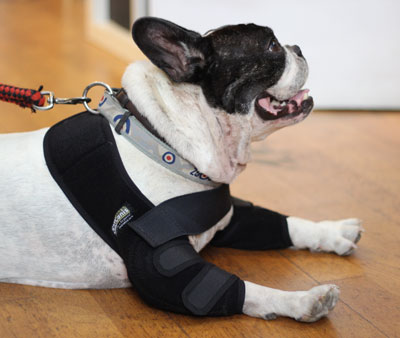
Often, the region in which the diseased joint is located is usually somewhat deformed due to osteophytes and muscle atrophy caused by the absence of physical activity. Many times a characteristic snap is detected when we move it. Through the radiological study, the animal health specialist will be able to determine the severity of osteoarthritis and establish the most appropriate treatment. Among the possible treatments, the appearance of specialized supports for some limbs that can effectively combat the deterioration of the animal’s quality of life stands out. The use of these supports is effective and has proven in countries such as the USA to be treatments as innovative as successful, however their use should be consulted with the veterinarian or animal physiotherapist.
Orthocanis Team
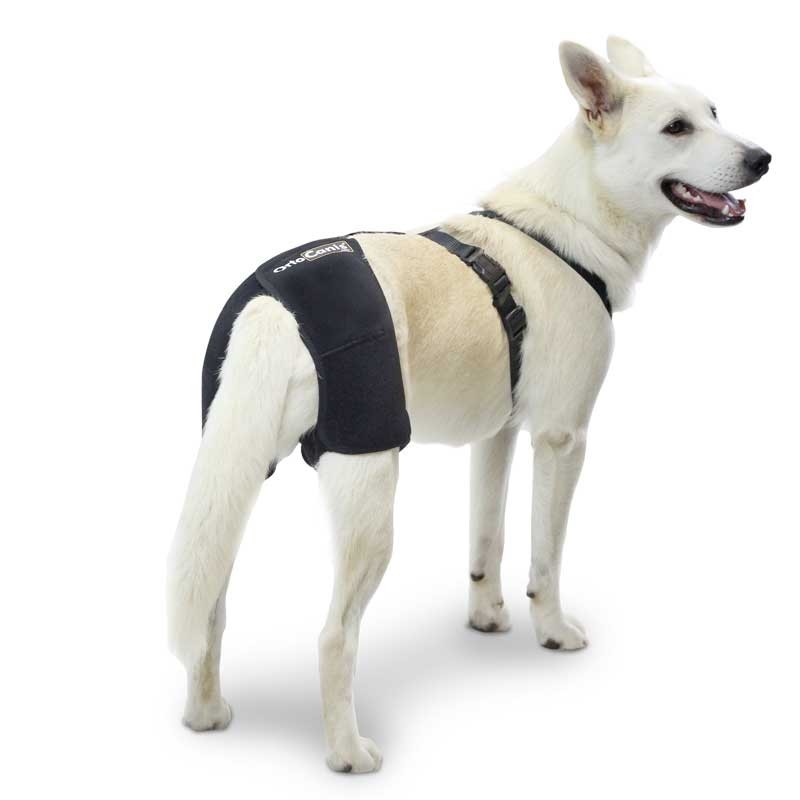
















 If we complement it with a correct hygiene (also important for health) and a careful education of the dog important for the family-dog relationship, we will have a set of aspects that will greatly improve the relationship with our dog, its quality of life and that of the whole family.
If we complement it with a correct hygiene (also important for health) and a careful education of the dog important for the family-dog relationship, we will have a set of aspects that will greatly improve the relationship with our dog, its quality of life and that of the whole family.
 cafes and restaurants. We have seen them but we have not heard them, nor have we smelled them nor have we noticed their presence until the owners of the animal have left the premises. The dog was missing the entire time he was in the restaurant. Nothing like the dogs that you can find in beach bars, which is one of the few places where they accept them, and not always, competing for the neighbor’s croquette or for the piece of ham that has fallen to the lady or for directly the grilled cuttlefish that have brought you and smell wonderful.
cafes and restaurants. We have seen them but we have not heard them, nor have we smelled them nor have we noticed their presence until the owners of the animal have left the premises. The dog was missing the entire time he was in the restaurant. Nothing like the dogs that you can find in beach bars, which is one of the few places where they accept them, and not always, competing for the neighbor’s croquette or for the piece of ham that has fallen to the lady or for directly the grilled cuttlefish that have brought you and smell wonderful.